What is alopecia? It’s no laughing matter for millions of Black American women

Jeff Kravitz/FilmMagic
Danita Peoples, Wayne State University
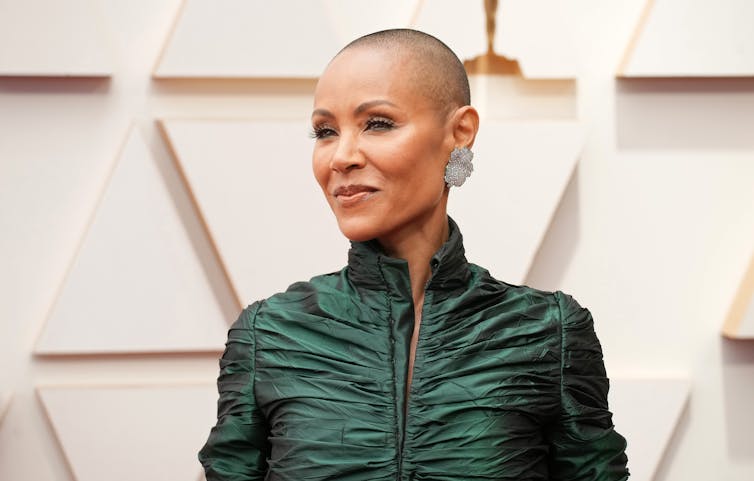
The Oscar slap that overshadowed the Academy Awards ceremony was sparked by a joke about Jada Pinkett Smith’s lack of hair – with husband Will Smith objecting violently to comedian Chris Rock mocking the actress’s shaved head.
Away from the recriminations over what could be perceived as a mean-spirited jibe and a disproportionate response, many people will sympathize with Pinkett Smith. As millions of women in the U.S. will attest, hair loss is no laughing matter.
The Conversation asked dermatologist Danita Peoples of Wayne State University’s School of Medicine about alopecia and why certain forms of it can disproportionately affect Black women.
1. What is alopecia?
Alopecia is a medical word that refers to hair loss generally. And there are descriptors added which can refer to where the hair loss is occurring, or to the cause of it. Traction alopecia, for example, is hair loss from trauma or chronic inflammatory changes to the hair follicles.
2. What causes alopecia?
Traction alopecia happens when there is trauma to the scalp, where the hair is being pulled or rubbed on a regular basis, causing inflammation around the hair follicles. This can lead to hair loss or thinning.
Alopecia areata describes hair loss to a particular area. It has different levels of severity, so there might be just a coin-sized area of hair loss on the scalp, or it could affect large areas. It can occur any place on the body.
Or it might result in complete hair loss on the scalp, alopecia totalis. Some people lose eyebrows or see a thinning of their eyelashes.
People can even have alopecia universalis, which is a loss of hair on the entire body.
Alopecia areata is considered an “immune-mediated” type of hair loss. The immune system is attacking the hair follicles. It has to do with T cells, the important white blood cells in the immune system.
And then other autoimmune disorders can have alopecia associated with them. This is the form of alopecia that Jada Pinkett Smith has said she has.
Lupus is an autoimmune disorder that can lead to hair loss. One type is systemic lupus erythematosus. Another type, discoid lupus erythematosus, primarily affects the skin and can cause hair loss with scarring on the scalp.
Thyroid abnormalities can be related to hair loss as well. In fact, when patients come to me with hair loss, the first test that I may order is a thyroid study.
3. Who does it affect?
Anyone can get alopecia. Alopecia areata can show up at any age, from children to adults, and both men and women. But it’s more likely to affect African Americans than white or Asian Americans. About 1 million people in the U.S. have alopecia areata.
Traction alopecia can affect people in certain professions, like ballerinas, who wear their hair up in buns all the time. The pressure and friction from sports headgear, like helmets or baseball caps, can also cause hair loss. And in some parts of northern Europe, where it is common for people to pull their hair back tight on a regular basis, there are higher rates of traction alopecia. Traction alopecia affects one-third of women of African descent, making it the most common type of alopecia affecting Black women.
4. Why is traction alopecia so common among Black women?
That is due to certain hair styling practices that Black women use on their hair – wearing tight weaves or extensions, straightening with heat, that sort of thing. Hair is a big deal among African American women in a way that it isn’t for others. When I was growing up, my older relatives told us girls that our hair was our “crowning glory.” And they made a big deal about us keeping our hair looking stylish and well groomed, and that usually meant straightening it.
But I believe there’s less pressure than there used to be for Black women to keep our hair straightened, in the workplace or elsewhere.
5. How is alopecia treated?
It depends on the cause. There are injected or topical corticosteroids for alopecia areata. If it’s due to a nutritional deficiency, like iron or protein, obviously you simply need to correct the deficiencies with supplements or by changing the diet. When it is caused by traction or discoid lupus, if you don’t treat the inflammation on the scalp soon enough, the hair loss can become permanent.
[Over 150,000 readers rely on The Conversation’s newsletters to understand the world. Sign up today.]
When it comes to traction, though, it’s much more about eliminating the practices that cause the problem in the first place. What’s happening now is more people are aware of the downsides of chemical or heat applications to straighten the hair and are using those damaging processes less.
One thing that may help is the CROWN Act, legislation introduced last year, which the U.S. House passed on March 18, 2022. That would make it illegal to discriminate against people wearing natural styles, such as afros and braids, so I am hopeful that it will contribute to a lot less traction alopecia in the future.
Danita Peoples, Clinical Associate Professor of Dermatology, Wayne State University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.