Monkeypox is caused by a virus that, despite periodic outbreaks, is not thought to spread easily from person to person and historically has not spurred long chains of transmission within communities. Now, many researchers are left scratching their heads as to why monkeypox seems to be propagating so readily and unconventionally in the current global outbreak.
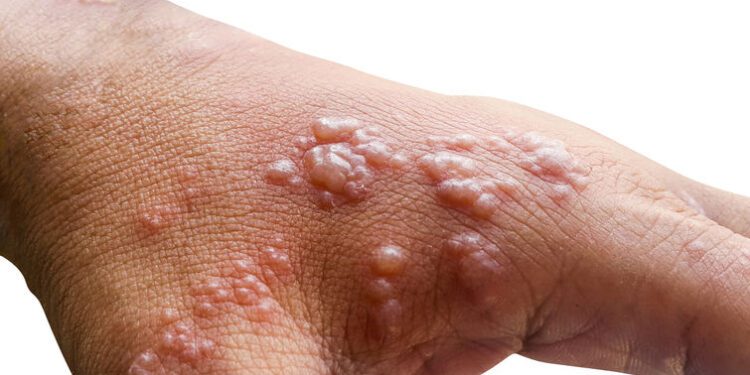
The monkeypox virus typically spreads through direct contact with respiratory secretions, such as mucus or saliva, or skin lesions. Skin lesions traditionally appear soon after infection as a rash – small pimples or round papules on the face, hands or genitalia. These lesions may also appear inside the mouth, eyes and other parts of the body that produce mucus. They can last for several weeks and be a source of virus before they are fully healed. Other symptoms usually include fever, swollen lymph nodes, fatigue and headache.
I am an epidemiologist who studies emerging infectious diseases that cause outbreaks, epidemics and pandemics. Understanding what’s currently known about how monkeypox is transmitted and ways to protect yourself and others from infection can help reduce the spread of the virus.
How is this outbreak different from prior ones?
The current monkeypox epidemic is a bit unusual in a few ways.
First, the sheer scope of the current epidemic, with over 25,000 cases worldwide as of early August and in countries where the virus has never appeared, sets it apart from previous outbreaks. Monkeypox is endemic to specific areas in central and western Africa, where cases occur sporadically and outbreaks are usually contained and quickly burn out. In the current outbreak, global spread has been rapid. Young men, mostly ages 18 to 44, account for the majority of cases, and over 97% identify as men who have sex with men (MSM). Some superspreading events associated with air travel, international gatherings and multiple-partner sexual encounters contributed to early transmission of the virus.
Second, the way symptoms are appearing may facilitate spread among people who don’t yet know they are infected. Most patients reported mild symptoms without fever or swollen lymph nodes, symptoms that typically appear before a skin rash is visible. While most people do develop skin lesions, many reported having only a single papule that was often obscured inside a mucosal area, such as inside the mouth, throat or rectum, making it easier to miss.
A number of people reported no symptoms at all. Asymptomatic infections are more likely to go undiagnosed and unreported than those with symptoms. But it is not yet known how asymptomatic individuals may be contributing to spread or how many asymptomatic cases may be undetected so far.
Who is at risk of getting monkeypox?
For most people, the risk of getting monkeypox is currently low. Anyone who has prolonged, close contact with an infected person is at risk, including partners, parents, children or siblings, among others. The most common settings for transmission are within households or health care settings.
Because of sustained transmission within the community of men who have sex with men, they are considered an at-risk group, and targeted recommendations can help allocate resources and limit transmission. While monkeypox is spreading primarily among MSM, this does not mean that the virus will remain confined to this group or that it won’t jump to other social networks. The virus itself has no regard for age, gender, ethnicity or sexual orientation.
Anyone who comes into direct contact with the monkeypox virus is at risk of being infected. New cases are recorded daily, with additional countries and regions reporting their first cases and already affected countries observing a continued rise in infections.
As with most infections, other factors, such as the amount of viral exposure, type of contact and individual immune response, play a role in whether an infection takes hold.
Is monkeypox an STI?
While sexual encounters are currently the predominant mode of transmission among reported cases, monkeypox is not a sexually transmitted infection. STIs are spread primarily through sexual contact, while monkeypox can spread through any form of prolonged, close contact.
Close contact that transmits the monkeypox virus involves encounters that are typically more intimate or involved than having a casual conversation or standing next to someone in an elevator. Transmission requires exchange of mucosal fluids or direct contact with the virus in sufficient quantity to seed an infection. This could occur through physical contact during kissing or cuddling.
NIAID/Flickr, CC BY
Because sexual encounters involve direct skin-to-skin physical contact where bodily fluids may be exchanged, these close encounters can transmit viruses more easily. Recently, monkeypox DNA has been detected in feces and various body fluids, including saliva, blood, semen and urine. But the presence of viral DNA does not necessarily mean that the virus can infect someone else. Transmission from these sources is still under investigation.
As the virus moves through populations, public health officials focus on getting the message out to the most at-risk and hardest hit communities about how to stay safe. Currently, breaking the transmission chain among sexual contacts is a priority, including but not limited to MSM communities. Targeted messaging is meant to protect the health of a specific group, not to stigmatize the intended audience.
Other modes of transmission may play a greater role outside the MSM community. Household transmission, where individuals may come into close contact with infected people or contaminated items, is one of the most common types of exposure. Research is ongoing into the potential airborne and respiratory droplet spread of monkeypox in the current situation.
Outbreaks are dynamic situations that evolve over time, which is why public health messages may change as the epidemic progresses. Not every outbreak looks or behaves the same way – even pathogens seen in previous outbreaks can be different the next time around. As researchers learn more about how the disease is transmitted and identify changes in patterns of spread, public health officials will provide updates about specific forms of contact, behaviors or other factors that could increase infection risk. While changing guidelines can be frustrating or confusing, keeping up to date with the latest recommendations can help you protect yourself and stay safe.
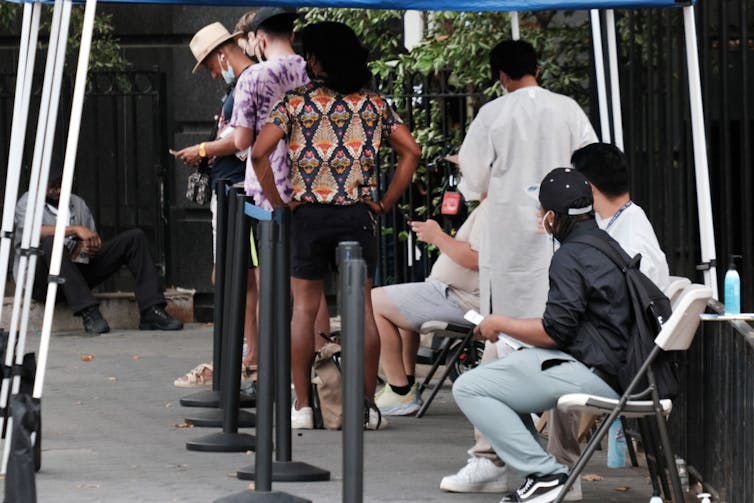

Spencer Platt/Getty Images News via Getty Images
What do I do if I’ve been exposed to monkeypox?
Anyone who has been infected can help contain spread by isolating from others, including pets. Covering skin lesions, wearing a mask in shared spaces and decontaminating shared surfaces or items, such as bed linens, dishes, clothes or towels, can also reduce spread.
You can also help interrupt the transmission chain by participating in contact tracing, notifying public health officials of others who may have been exposed through you, which is a basic tenet and common practice of disease control.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has further guidance on how to control monkeypox spread in both household settings and shared living facilities.
Lastly, getting vaccinated as soon as possible can still protect you from severe illness even if you’ve already been infected.
Rebecca S.B. Fischer, Assistant Professor of Epidemiology, Texas A&M University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.