Here’s what allergy sufferers can expect in the future
Bob Sacha/Corbis Documentary via Getty Images
Yingxiao Zhang, University of Michigan and Allison L. Steiner, University of Michigan
Brace yourselves, allergy suffers – new research shows pollen season is going to get a lot longer and more intense with climate change.
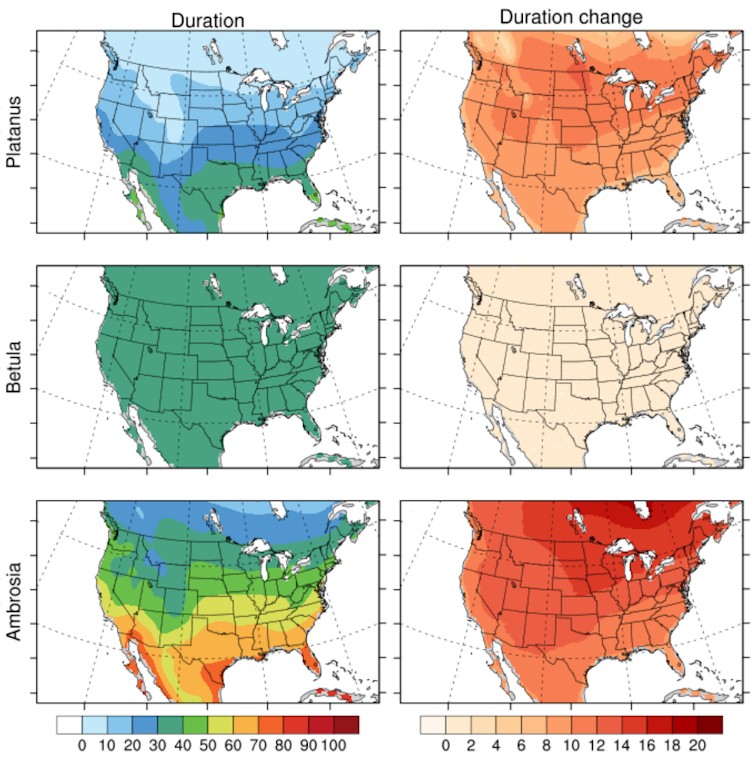
Our latest study finds that the U.S. will face up to a 200% increase in total pollen this century if the world continues producing carbon dioxide emissions from vehicles, power plants and other sources at a high rate. Pollen season in general will start up to 40 days earlier in the spring and last up to 19 days longer than today under that scenario.
As atmospheric scientists, we study how the atmosphere and climate affect trees and plants. While most studies focus on pollen overall, we zoomed in on more than a dozen different types of grasses and trees and how their pollen will affect regions across the U.S. in different ways. For example, species like oak and cypress will give the Northeast the biggest increase, but allergens will be on the rise just about everywhere, with consequences for human health and the economy.
Zhang and Steiner, 2022
If your head is pounding at just the thought of it, we also have some good news, at least for knowing in advance when pollen waves are coming. We’re working on using the model from this study to develop more accurate local pollen forecasts.
Why pollen is increasing
Let’s start with the basics. Pollen – the dust-like grains produced by grasses and plants – contains the male genetic material for a plant’s reproduction.
How much pollen is produced depends on how the plant grows. Rising global temperatures will boost plant growth in many areas, and that, in turn, will affect pollen production. But temperature is only part of the equation. We found that the bigger driver of the future pollen increase will be rising carbon dioxide emissions.
The higher temperature will extend the growing season, giving plants more time to emit pollen and reproduce. Carbon dioxide, meanwhile, fuels photosynthesis, so plants may grow larger and produce more pollen. We found that carbon dioxide levels may have a much larger impact on pollen increases than temperature in the future.

Famartin/Wikimedia, CC BY-ND
Pollen changes will vary by region
We looked at 15 different pollen types, rather than treating all pollen the same as many past studies have.
Typically, pollination starts with leafy deciduous trees in late winter and spring. Alder, birch and oak are the three top deciduous trees for causing allergies, though there are others, like mulberry. Then grasses come out in the summer, followed by ragweed in late summer. In the Southeast, evergreen trees like mountain cedar and juniper (in the cypress family) start in January. In Texas, “cedar fever” is the equivalent of hay fever.
We found that in the Northeast, pollen seasons for a lot of allergenic trees will increasingly overlap as temperatures and carbon dioxide emissions rise. For example, it used to be that oak trees would release pollen first, and then birch would pollinate. Now we see more overlap of their pollen seasons.
In general, pollen season will change more in the north than in the south, because of larger temperature increases in northern areas.
Southeastern regions, including Florida, Georgia and South Carolina, can expect large grass and weed pollen increases in the future. The Pacific Northwest is likely to see peak pollen season a month earlier because of the early pollen season of alder.
Silver lining: We can improve pollen forecasting
Most pollen forecasts right now provide a very broad estimate. Part of the problem is that there aren’t many observing stations for pollen counts. Most are run by allergy clinics, and there are less than 100 of these stations distributed across the country. Michigan, where we live, doesn’t have any.
It’s a very labor-intensive process to actually measure different types of pollen. As a result, current forecasts have a lot of uncertainties. These likely are based in part on what a station has observed in the past and the weather forecast.

HelenaAnna/Wikimedia, CC BY-ND
Our model, if integrated into a forecasting framework, could provide more targeted pollen forecasts across the country.
We can estimate where the trees are from satellite data and on-the-ground surveys. We also know how temperature influences when pollen comes out – what we call the phenology of the pollen. With that information, we can use meteorological factors like wind, relative humidity and precipitation to figure out how much pollen gets into the air, and atmospheric models can show how it moves and blows around, to create a real-time forecast.
All of that information allows us to look at where pollen might be in space and time, so people dealing with allergies will know what’s coming in their area.
We’re currently talking with a National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration lab about ways to integrate that information into a tool for air quality forecasting.
Bob Sacha/Corbis Documentary via Getty Images
There are still some unknowns when it comes to long-term pollen projections. For example, scientists don’t fully understand why plants produce more pollen in some years than others. There’s not a good way to include that in models. It’s also not fully clear how plants will respond if carbon dioxide levels go through the roof. Ragweed and residential trees are also hard to capture. There are very few ragweed surveys showing where these plants are growing in the U.S., but that can be improved.
Pollen levels are already on the rise
A study in 2021 found that the overall pollen season was already about 20 days longer in North America than it was in 1990 and pollen concentrations were up about 21%.
Increasing pollen levels in the future will have a much broader impact than a few sniffles and headaches. Seasonal allergies affect about 30% of the population, and they have economic impacts, from health costs to missed working days.
[Over 150,000 readers rely on The Conversation’s newsletters to understand the world. Sign up today.]
Yingxiao Zhang, Ph.D. Student in Atmospheric Science, University of Michigan and Allison L. Steiner, Professor of Atmospheric Science, University of Michigan
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
















